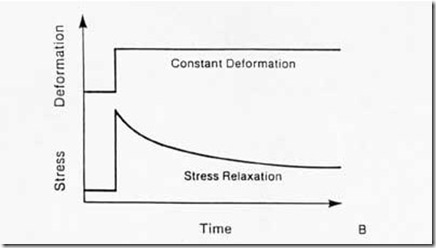
Stress relaxation is the more relevant property for sealing products such as O-ring , rubber seals and rubber gaskets. When rubber is held at constant deformation, there is a decrease in stress as a function of time.This phenomenon can be of great impoertance in sealing application,where the material of the seal is required to maintain a specific level of sealing force to prevent leakage. Stress relaxation can be the dominant factor that limits the effect life of rubber seals and rubber gaskets.
Stress relaxation is usually defined as the loss in stress expressed as a percentage of the initial stress. Thus
stree relaxation = 100*(So – St)/So
So is initial stress
St is stress at time t
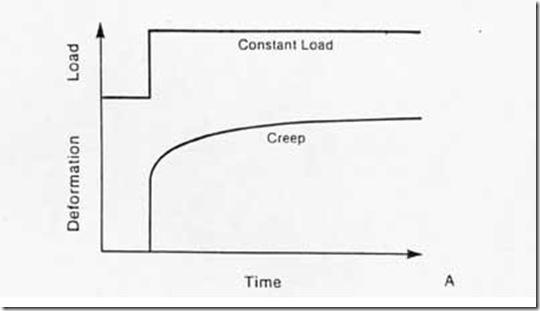
Stress relaxation and creep rate are related to one another if the shape of the force-deflection curve is known. According to this the relationship between the two parameter is determined by the incremental stiffness at the point on the force-deflection curve relevant to the stress relaxation or creep measurement .Thus
where C is the creep rate, S is the stress relaxation rate .Since it has been established that creep and stress relaxation can be related in this way,in the next topic i will be following discussion both are referred to as relaxation processes.
Pic. Stress relaxation phenomenon
**Ref. http://www.engin.umich.edu/class/bme332/ch10ligten/bme332ligamenttendon.htm



 = 1.13 for saturate backbone hydrocarbon that identify according to ASTM D 1418 designation "M" ; e.g., EPDM and 1.22 for unsaturated elastomer ASTM D1418 designation " R" ; e.g., NBR , SBR , NR
= 1.13 for saturate backbone hydrocarbon that identify according to ASTM D 1418 designation "M" ; e.g., EPDM and 1.22 for unsaturated elastomer ASTM D1418 designation " R" ; e.g., NBR , SBR , NR